Introduction
In this tutorial, we will learn about how to install Cockpit on CenOS 7 using 7 easy steps. Cockpit is one of the server monitoring tool provided by Red Hat. Server monitoring tools in Linux are utilities designed to monitor the performance, health and availability of Linux servers. There are severe open source monitoring tools option available. few of them are:
- Nagios
- Zabbix
- Performance Co Pilot
- Cockpit (Red hat)
- Landscape (Ubuntu)
![How to Install Cockpit on CentOS 7: [7 Easy Steps]](https://www.linuxnasa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/cockpit-linux-1.jpg)
What is Cockpit?
Cockpit is an open source, web based server management tool that provides an easy-to-use interface for monitoring and managing Linux servers. It offers a range of features that make it a powerfull tool for both beginners and experienced Linux administrator. Some key features of Cockpit are:
Real-time System Metrics: It displays real time system metrics like CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity and network activity.
System Logs: It provides access to system logs, making it easy to troubleshoot issues.
Service Management: It allows us to start, stop, enable and disable system services directly from Cockpit.
Software Update: It allows us to manage software updates and packages. We can view available updates, apply them and check for security updates.
Storage Management: It allows us to manage storage devices, partitions and file systems through Cockpit.
How to Install Cockpit on CentOS 7: [7 Easy Steps]
Also read: 10+ Important Linux Commands with Examples
Prerequisite
- Linux CentOS Distro installed
- Yum repository Enabled
- Must have root Privilege
Step-1: Check Linux Distro
In this step, we will check which Linux distro our system has. Make sure it is using CentOS distro as other Linux distros have different repositories from where Linux packages can be install so yum repo may bot work for other distros.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
Step-2: Search Cockpit in the repository
In this step, we will search for the cockpit package in the yum repository as shown below.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# yum search cockpit Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast Determining fastest mirrors * base: centos.mirror.far.fi * centos-qemu-ev: centos.mirror.far.fi * epel: mirror.cspacehostings.com * extras: centos.mirror.far.fi * updates: centos.mirror.far.fi ================================================================ N/S matched: cockpit ================================================================ cockpit-bridge.x86_64 : Cockpit bridge server-side component cockpit-composer.noarch : Composer GUI for use with Cockpit cockpit-dashboard.x86_64 : Cockpit remote servers and dashboard cockpit-doc.x86_64 : Cockpit deployment and developer guide cockpit-docker.x86_64 : Cockpit user interface for Docker containers cockpit-kubernetes.x86_64 : Cockpit user interface for Kubernetes cluster cockpit-machines.x86_64 : Cockpit user interface for virtual machines cockpit-machines.noarch : Cockpit user interface for virtual machines cockpit-machines-ovirt.noarch : Cockpit user interface for oVirt virtual machines cockpit-packagekit.x86_64 : Cockpit user interface for package updates cockpit-packagekit.noarch : Cockpit user interface for packages cockpit-pcp.x86_64 : Cockpit PCP integration cockpit-storaged.noarch : Cockpit user interface for storage, using udisks cockpit-subscriptions.noarch : Cockpit subscription user interface package cockpit-system.noarch : Cockpit admin interface package for configuring and troubleshooting a system cockpit-tests.x86_64 : Tests for Cockpit cockpit-ws.x86_64 : Cockpit Web Service cockpit-ws.i686 : Cockpit Web Service subscription-manager-cockpit.noarch : Subscription Manager Cockpit UI cockpit.x86_64 : Web Console for Linux servers Name and summary matches only, use "search all" for everything.
Step-3: Install Cockpit Package
In this step, we will install couple of cockpit packages available in the yum repository using below command.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# yum install cockpit cockpit-system cockpit-storaged cockpit-pcp Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register. Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile epel/x86_64/metalink | 30 kB 00:00:00 * base: ftp.funet.fi * centos-qemu-ev: ftp.funet.fi * epel: www.nic.funet.fi * extras: ftp.funet.fi * updates: ftp.funet.fi base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 centos-ceph-luminous | 3.0 kB 00:00:00 centos-openstack-rocky | 3.0 kB 00:00:00 centos-qemu-ev | 3.0 kB 00:00:00 docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00 epel | 4.7 kB 00:00:00 extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 (1/5): extras/7/x86_64/primary_db | 250 kB 00:00:00 (2/5): docker-ce-stable/7/x86_64/primary_db | 114 kB 00:00:00 (3/5): epel/x86_64/updateinfo | 1.0 MB 00:00:00 (4/5): epel/x86_64/primary_db | 7.0 MB 00:00:00 (5/5): updates/7/x86_64/primary_db | 22 MB 00:00:00 Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package cockpit.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos will be installed --> Processing Dependency: cockpit-ws for package: cockpit-195.12-1.el7.centos.x86_64 --> Processing Dependency: cockpit-bridge for package: cockpit-195.12-1.el7.centos.x86_64 ---> Package cockpit-pcp.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos will be installed .......................... .......................... .......................... ---> Package systemd-sysv.x86_64 0:219-73.el7.1 will be updated ---> Package systemd-sysv.x86_64 0:219-78.el7_9.7 will be an update --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ===================================================================================================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size ===================================================================================================================================================== Installing: cockpit x86_64 195.12-1.el7.centos extras 51 k cockpit-pcp x86_64 195.12-1.el7.centos extras 96 k ............................................................................... ............................................................................... systemd-libs x86_64 219-78.el7_9.7 updates 419 k systemd-sysv x86_64 219-78.el7_9.7 updates 97 k Transaction Summary ===================================================================================================================================================== Install 4 Packages (+39 Dependent packages) Upgrade ( 4 Dependent packages) Total download size: 16 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: Delta RPMs disabled because /usr/bin/applydeltarpm not installed. (1/47): cockpit-195.12-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm | 51 kB 00:00:00 (2/47): cockpit-bridge-195.12-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm | 555 kB 00:00:00 (3/47): cockpit-pcp-195.12-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm | 96 kB 00:00:00 .................................. .................................. .................................. (46/47): udisks2-lvm2-2.8.4-1.el7.x86_64.rpm | 62 kB 00:00:00 (47/47): volume_key-libs-0.3.9-9.el7.x86_64.rpm | 141 kB 00:00:00 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Installed: cockpit.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos cockpit-pcp.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos cockpit-storaged.noarch 0:195.12-1.el7.centos cockpit-system.noarch 0:195.12-1.el7.centos Dependency Installed: cockpit-bridge.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos cockpit-ws.x86_64 0:195.12-1.el7.centos device-mapper-multipath.x86_64 0:0.4.9-136.el7_9 device-mapper-multipath-libs.x86_64 0:0.4.9-136.el7_9 .............................................................................................. ................................................................................................ Dependency Updated: kpartx.x86_64 0:0.4.9-136.el7_9 systemd.x86_64 0:219-78.el7_9.7 systemd-libs.x86_64 0:219-78.el7_9.7 systemd-sysv.x86_64 0:219-78.el7_9.7 Complete!
Step-4: Run Cockpit
In this step, once the cockpit is installed successfully, run the cockpit using below command. By default, cockpit does not come with service instead it comes with socket which means that it is going to listen on the cockpit boards and once the activity is detected on that board, it will open.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/cockpit.socket to /usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket.
Step-5 : Configure Firewall
In this step, we will configure the firewall for Cockpit using below command.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service cockpit success
Step-6: Restart the Firewall
In this step, we will restart the firewall using below command.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
Step-7: Access Cockpit in Browser
In this step, we will access the cockpit in a browser. The default port on which cockpit is accessible is 9090. First execute ip addr command and get the eth0 IP as shown below.
[root@linuxnasa-server ~]# ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether ea:12:1e:fe:3c:5e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.29.151.130/27 brd 10.29.151.130 scope global noprefixroute dynamic eth0 valid_lft 67103sec preferred_lft 67103sec
Next, open the browser and type http://<system-eth0-ip>:<cockpit-port-number> to access the cockpit GUI interface.
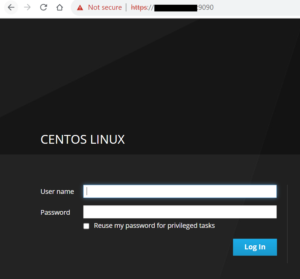
Hit the url and you will see the Cockpit interface will appear as shown below. Login to the GUI using your system credential .
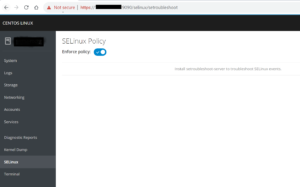
You will be able to see the cockpit GUI page where we see a nice overview of everything that is happening on the system.
Summary
We learnt about how to install Cockpit on Linux CenOS distrol. Similarly we can install this monitoring tool on any other Linux distros. You can refer to Cockpit Install Guide for installing on any distros.
