![Python Comparing Tuples [Step by Step Guide] - linuxnasa](https://www.linuxnasa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/python-import-class-from-another-file-step-by-step-guide-2-300x169.jpg)
In this tutorial, we will learn about Python comparing tuples using step by step guide. In Python, tuple is a data structure which is also an iterable object. There are use cases or requirement in our day to day task where we have to do the comparison of different tuples. There are different built-in functions and modules available like Numpy module which can be utilized to compare the tuples. In this tutorial, we will cover built-in functions and comparison operator to compare the tuples.
Python Comparing Tuples [Step by Step Guide] – linuxnasa
There are multiple ways to compare tuples. We will learn about three basic and most used methods for comparing tuples. These methods helps us solved many requirements. These methods are:
- Comparison Operators (==, !=, <, <=, >, >=)
- all() Function
- any() Function
Using Comparison Operators
There are 6 comparison operators available which can be used to compare tuples. These operators are listed in below table. We will look at the usage of each operator using examples.
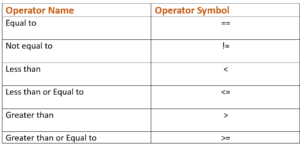
Before jumping into the implementation of tuple comparison using different operators, It is import to know that in Python, tuple comparison is performed lexicographically. It means tuples are compared element-wise. It will compare first element of both tuple, if the first element satisfy the condition, overall output is returned as true else false otherwise. Let us look at examples now to grab more understanding on the concept.
Example-1:
values1 = (4,10,4,7) values2 = (5,6,3,1) print ("Equal to Operation output: ", values1 == values2) print ("Not equal to Operation output: ", values1 != values2) print ("Less than Operation output: ", values1 < values2) print ("Less than or equal to Operation output: ", values1 <= values2) print ("Greater than Operation output: ", values1 > values2) print ("Greater than or equal to Operation output: ", values1 >= values2)
Equal to Operation output: False Not equal to Operation output: True Less than Operation output: True Less than or equal to Operation output: True Greater than Operation output: False Greater than or equal to Operation output: False
Using all() Function
In Python, all() is a built-in function which provides the ability to compare the iterable objects (list, tuples, set and dictionary). It returns true if all elements of iterable are true else it will return false. Let us see below example to implement the concept. To compare the tuples element-wise, we will use zip() function which is again a built-in function in Python. If all elements satisfy the condition, it will return true. If any of the element does not satisfy the condition, it will return false. Checkout the below examples.
Example-2
Let us utilize same tuples from example-1 as shown below. We will then apply each comparison operators on these tuple and see the output it returns.
values1 = (4,1,2,9)
values2 = (5,6,3,7)
Equal to
print (f"Equal to Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Equal to Operation output: False
print (f"Not equal to Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Not equal to Operation output: False
print (f"Less than Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Less than Operation output: False
print (f"Less than or equal to Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Less than or equal to Operation output: False
print (f"Greater than Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Greater than Operation output: False
print (f"Greater than or equal to Operation output: {all(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")Greater than or equal to Operation output: False
Using any() Function
In Python, just like all(), any() is also a built-in function which is used to compare the iterable objects. any() function too can be used along with zip() function to do the element-wise comparison of iterable objects. In the below example, we have taken two tuple and doing the comparison using any() function. If any one if the element in iterable object satisfy the condition, overall outcome will be returned as true, false otherwise.
Example-3
values1 = (4,1,2,9) values2 = (5,6,3,7) print (f"Equal to Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}") print (f"Not equal to Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}") print (f"Less than Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}") print (f"Less than or equal to Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}") print (f"Greater than Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}") print (f"Greater than or equal to Operation output: {any(x < y for x, y in zip(values1, values2) )}")
OUTPUT
Equal to Operation output: True Not equal to Operation output: True Less than Operation output: True Less than or equal to Operation output: True Greater than Operation output: True Greater than or equal to Operation output: True
Summary
Reference – docs.python.org

